Contents
What is an Essential Plant Nutrient and How Does it Actually Work?
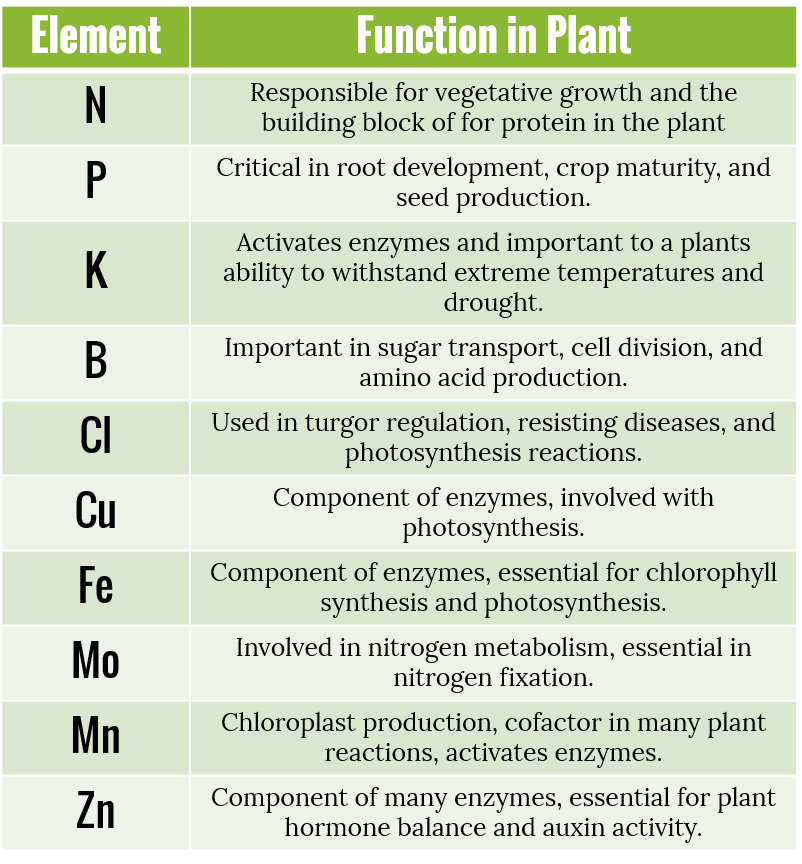
Plants require a range of essential nutrients for their growth and development. These nutrients are classified into two main categories: macronutrients and micronutrients. Each nutrient serves a specific function in the plant’s life cycle. Here is an overview of essential plant nutrients and their functions:
Macronutrients:
- Nitrogen (N):
- Function: Nitrogen is a vital component of chlorophyll, the green pigment responsible for photosynthesis. It promotes leafy growth, protein synthesis, and overall plant development.
- Phosphorus (P):
- Function: Phosphorus is essential for energy transfer within the plant and plays a crucial role in root development, flowering, and fruiting. It aids in the formation of DNA and RNA.
- Potassium (K):
- Function: Potassium regulates various physiological processes in plants, including water uptake, enzyme activation, and carbohydrate transport. It enhances disease resistance and overall plant health.
- Calcium (Ca):
- Function: Calcium is essential for cell wall structure and stability. It prevents disorders like blossom end rot in tomatoes and improves root and shoot development.
- Magnesium (Mg):
- Function: Magnesium is a central component of chlorophyll and is involved in photosynthesis. It also activates enzymes necessary for plant growth and nutrient uptake.
- Sulfur (S):
- Function: Sulfur is a component of amino acids, vitamins, and coenzymes. It plays a role in protein synthesis and is important for overall plant health.
Micronutrients (Trace Elements):
- Iron (Fe):
- Function: Iron is essential for chlorophyll synthesis and photosynthesis. It is involved in electron transport within plant cells.
- Manganese (Mn):
- Function: Manganese activates enzymes that are necessary for photosynthesis, respiration, and nitrogen metabolism.
- Zinc (Zn):
- Function: Zinc is a cofactor for many enzymes involved in DNA synthesis, protein production, and growth regulation.
- Copper (Cu):
- Function: Copper is required for electron transfer reactions in plant cells. It aids in lignin formation and is involved in reproductive processes.
- Boron (B):
- Function: Boron is crucial for cell elongation, flower formation, and the metabolism of carbohydrates. It also aids in the uptake of other nutrients.
- Molybdenum (Mo):
- Function: Molybdenum is essential for the conversion of nitrate (NO3-) into amino acids within the plant. It plays a role in nitrogen metabolism.
- Chlorine (Cl):
- Function: Chlorine is involved in photosynthesis, regulating stomatal openings, and maintaining ionic balance in plant cells.
These essential nutrients are taken up by plants through their roots from the soil or through foliar application. A deficiency or excess of any of these nutrients can lead to various growth disorders, reduced yield, and overall plant health issues. Proper nutrient management is essential for healthy and productive plant growth. Soils should be tested, and fertilizers or soil amendments should be applied as needed to ensure that plants receive the right balance of essential nutrients.
The first section of this article is to provide a conclusion in which the author states that everyone should start using an essential plant nutrient plan today to supercharge their productivity and creativity.
A few benefits of taking a plant nutrient plan are that it can help you sleep better, reduce stress, and boost your brain power.
What are Essential Plant Nutrients and Why Are They Important?
Plant nutrients are essential nutrients that plants require in order to grow. They are necessary for the growth and development of the plant, which is why it is important to provide them.
The most common plant nutrients include nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, sulfur, calcium and magnesium.
Plant nutrients are the factors that plants need to grow. They are essential for plant growth and development. Without them, plants will not be able to produce their own food.
It is important to know what plant nutrients are and why they are important. This article will look at the different types of plant nutrients and their importance in plant growth.
Plant growth is a process that involves three essential steps: germination, vegetative growth, and reproductive growth. The first step involves the germination of a seed, which requires light to break down the seed’s stored food reserves into usable energy for the new plant. The second step is vegetative growth where plants grow in height and width; this phase also has two sub-phases: leafy green plants grow their leaves while flower-bearing plants produce flowers. The third step is reproductive growth where plants produce seeds or fruit, depending on whether they’re flowering or not.
How Essential Plant Nutrients Help
Plants need nutrients to grow and thrive. Essential nutrients are the components that plants require for their growth and development.
– Plants use essential nutrients in their cell walls to create strong, flexible structures that can resist environmental pressures
– Plants use essential plant nutrients in their leaves as a source of energy for photosynthesis
– Plants need essential plant nutrients to make flowers and fruit
– Plants need essential plant nutrients to produce seeds for reproduction
– Essential plant nutrients are necessary for the process of photosynthesis
plant nutrients are essential ingredients that help plants grow and thrive. These nutrients can be found in all types of plants, but they are especially important for plant growth in areas like deserts or remote locations where water is scarce.
Some of the most amazing use cases of plant nutrients include:
– Plants with a higher nutrient content have been shown to have higher yields, which means you’ll get more food for your money.
– Plants with a high nutrient content are able to resist disease better, so you won’t have to worry about your crops being wiped out by pests and diseases.
– Plants with a high nutrient content can grow taller and stronger, which will help them withstand harsh weather conditions like drought or frost.

